JUnit简介
一、简介
JUnit是由Erich Gamma和Kent Beck编写的一个回归测试框架,大多数开源框架都使用JUnit进行单元测试。
单元测试中的”单元”是指一个能独立完成一件事情的方法,这个方法不依赖上下文的影响。举例如下:
public class Math{
public int multi(int m, int n){
return m * n;
}
public int div(int m, int n){
return m / n;
}
}
上述代码中的multi()和div()方法可以看作不同的单元。
public class Math(){
private int m = 0;
private int n = 0;
public void setValue(int m, int n){
this.m = m;
this.n = n;
}
public int multi(){
return m * n;
}
public int div(){
return m / n;
}
}
上述代码中的multi()和div()方法不可以单独作为单元,因为它依赖于setValue方法给m和n赋值。
二、使用
1、下载junit.jar
2、常用注解
JUnit4使用@Before和@After注解分别来标识初始化和销毁的方法,使用@Test注解来标识需要测试的方法,在测试方法中要编写断言。
常用注解如下:
- @Before
使用此注解标识的方法在每个测试方法执行之前都会执行一次。
- @After
使用此注解标识的方法在每个测试方法执行之后都会执行一次。
@Before和@After标识的方法只能各有一个。
- @Test(expected=*.class)
使用此注解标识一个方法为测试方法。在JUnit4之前,对错误的测试只能通过fail()来产生一个错误,并在try块中用assertTrue(true)来测试,现在可以使用expected属性,该属性值是一个异常的类型。
- @Test(timeout=xxx)
使用此注解标识一个方法为测试方法。使用timeout属性指定超时时间(毫秒),如果测试方法在设置的时间内没有运行完,则测试失败。
- @Ignore
使用此注解标记的方法在测试中会被怱略,当测试的方法还没有实现或测试的方法已经过时时,可以用此注解标识。还可以为此注解传递一个String类型的参数,表明为什么会怱略这个测试方法,例如:@Ignore(“该方法已过时”)
3、常用断言
- assertEquals(expected, actual)
检查实际值(actual)是否与期望值(expected)相等;如果是比较两个对象是否相等,则使用对象的equals()方法判断。
- assertSame(expected, actual)
检查两个对象是否相等,使用内存地址判断。
- assertNotSame(expected, actual)
检查两个对象是否不相等,使用内存地址判断。
- assertNull(object)
检查一个对象是否为空。
- assertNotNull(object)
检查一个对象是否不为空。
- assertTrue(condition)
检查布尔条件的值是否为真。
- assertFalse(condition)
检查布尔条件的值是否为假。
4、示例
public class Math{
public static int multi(int m, int n){
return m * n;
}
public static int div(int m, int n){
return m / n;
}
}
其单元测试代码如下:
public class TestMath{
private int m = 0;
private int n = 0;
//初始化方法
@Before
public void init(){
this.m = 8;
this.n = 2;
}
//测试方法
@Test
public void multi(){
assertEquals(16, Math.multi(m, n));
}
//测试方法
@Test
public void div(){
assertEquals(4, Math.div(m, n));
}
//销毁方法
@After
public void destory(){
this.m = 0;
this.n = 0;
}
}
Run As -- JUnit Test结果:
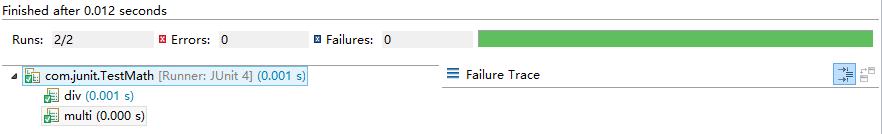
命令行下运行:
java -cp .;../lib/junit-4.11.jar;../lib/hamcrest-all-1.3.jar org.junit.runner.JUnitCore com.junit.TestMath
5、TestSuite
如果有多个测试类,一个一个地执行可能会耗费不少时间,可以使用TestSuite来一次执行多个测试类:
public class TestAll{
public static Test suite(){
TestSuite suite = new TestSuite("All Unit Tests");
//添加测试类
suite.addTest(new JUnit4TestAdapter(TestMath.class));
//suite.addTest(...);
return suite;
}
}
三、在Spring中使用JUnit4
在Spring3框架中使用JUnit4,除Spring.jar和junit.jar之处,还需要添加spring-test.jar和commons-logging.jar。
- 示例
applicationContext-service.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="sampleService" class="com.junit.SampleServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="666666"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
相关Java类:
public class Sample {
}
public interface ISampleService {
public List<Sample> getSamples();
}
public class SampleServiceImpl implements ISampleService{
@Override
public List<Sample> getSamples() {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}
测试类:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"/applicationContext-service.xml"})
public class ServiceTest extends AbstractTransactionalJUnit4SpringContextTests{
//依赖注入
@Resource(name="sampleService")
private ISampleService service;
//测试方法
@Test
public void getSamples(){
List<Sample> samples = service.getSamples();
Assert.assertNotNull(samples);
}
}
Run As -- JUnit Test结果:
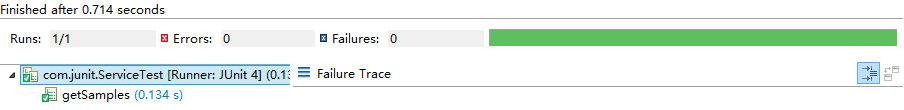
四、与Ant集成
JUnit可以与Ant集成使测试工作自动化。
1、Ant下载与安装
- 下载
下载地址:Apache Ant Download
- 安装
下载后解压,并配置系统环境变量:
ANT_HOME: F:\ProgramFiles\apache-ant
Classpath: %ANT_HOME%\lib;
Path: %ANT_HOME%\bin;
2、Ant配置简介
Ant通过XML文件来配置,通常XML中都要包含<project>和<target>两个元素。
-
project元素
-
name
项目名称
-
default
每个project都包含一个或多个target,一个target又包含一系列想要执行的task。使用Ant开始运行时,可以指定执行某个target,如果没有指定时则执行此属性中设置的默认target。
-
basedir
当前项目的基本路径,
.表示当前项目的根目录。
-
-
target元素
-
name
目标名称
-
depends
依赖的target
-
if
设置执行时的条件,满足此条件时执行
-
unless
设置执行时的条件,如果不满足此条件时则不执行
-
description
对目标(target)的描述
-
task
一小段任务
-
reference
引用,通过refid属性来引用在其他节点中定义的id
-
3、集成示例
- build.xml
<project name="MyProject" default="test" basedir=".">
<description>junit ant integration</description>
<!-- set global properties for this build -->
<property name="src" location="src"/>
<property name="build" location="build"/>
<property name="report" location="report"/>
<path id="required.classpath">
<fileset dir="./lib">
<include name="*.jar"/>
</fileset>
</path>
<target name="init">
<!-- Create the time stamp -->
<tstamp/>
<!-- Create the build directory structure used by compile -->
<mkdir dir="${build}"/>
<mkdir dir="${report}"/>
</target>
<target name="compile" depends="init" description="compile the source">
<!-- Compile the Java code from ${src} into ${build} -->
<javac srcdir="${src}" destdir="${build}" includeAntRuntime="false">
<classpath refid="required.classpath"/>
</javac>
</target>
<target name="test" depends="compile" description="junit test">
<available property="classExist" file="${build}/com/junit/TestMath.class"/>
<junit printsummary="yes" haltonfailure="yes">
<!-- dependencies jars -->
<classpath refid="required.classpath"/>
<!-- TestMath classpath -->
<classpath>
<pathelement location="${build}"/>
</classpath>
<test name="com.junit.TestMath" if="classExist" todir="${report}">
<formatter type="xml"/>
</test>
</junit>
<junitreport todir="${report}">
<fileset dir="${report}">
<include name="TEST-*.xml"/>
</fileset>
<report format="frames" todir="${report}/html"/>
</junitreport>
</target>
<target name="clean" description="clean up">
<!-- Delete the ${build} and ${report} directory trees -->
<delete dir="${build}"/>
<delete dir="${report}"/>
</target>
</project>
如果Build Failed可以使用ant test -d命令(debug),查看具体错误原因。
<test>标签中的todir属性为 report 的生成目录,在<junitreport>中会根据这些文件(TEST-xxx.xml)来生成报告。
如果相批量运行TestCase,则可以使用<batchtest>来替代<test>:
<batchtest todir="${report}">
<formatter type="xml"/>
<fileset dir="${build}">
<include name="**/*TestMath.class"/>
</fileset>
</batchtest>
使用ant test命令开始运行,ant clean命令清除数据;报告结果如下:
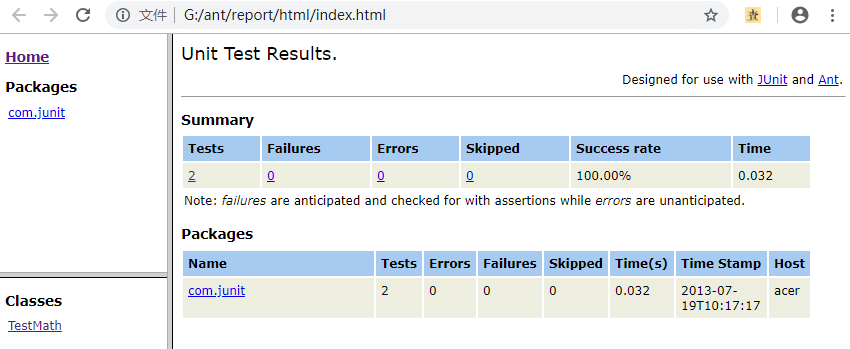
附:
Maven Repository: Hamcrest All
Maven Repository: Spring TestContext Framework
Maven Repository: Spring Context