Java注解
一、简介
Annotation可以用来为程序中的类、方法、成员变量等设置元数据,使得开发者在不改变原有逻辑的情况下,在源文件中嵌入一些补充的信息。解析和处理Annotation的工具被称为APT(Annotation Processing Tool)。
Java中使用Annotation接口代表程序元素的注解,该接口是所有Annotation类型的父接口。
二、JDK注解
JDK在java.lang包中提供了三个基本的Annotation:@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnings和四个Meta Annotation:@Retention、@Target、@Documented、@Inherited。
1、基本Annotation
@Override
@Override注解用来指定方法覆载,它可以强制一个子类必须覆盖父类的某个方法。此注解只能作用于方法。
@Override
public String toString() {
return "my class";
}
@Deprecated
@Deprecated注解用来表示某个类、方法等已过时,当其他程序中使用此注解标注的程序元素时,编译器会显示警告。

@SuppressWarnings
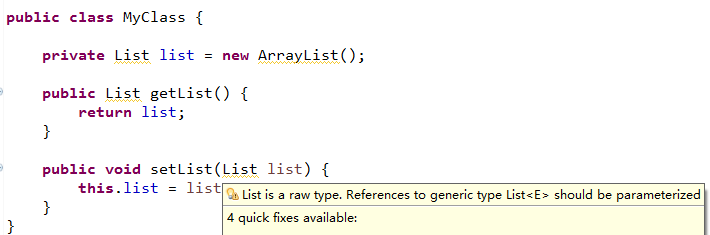
@SuppressWarnings注解可以让编译器不显示被此注解标记的程序元素(包括该程序元素的子元素)的警告信息。例如:如果在某个类上标注不显示某个编译警告,在该类的某个方法上标注不显示另外一个编译警告,那么在该方法上将不会显示这两个编译警告。
2、元Annotation
元Annotation用于修饰Annotation定义,有以下四个:
-
@Retention@Retention注解用来指定Annotation的存在时期;在使用时必须为此注解的成员变量value设置值,该值为RetentionPolicy的枚举值。RetentionPolicy有三个值:-
SOURCE源码级别,编译器会直接丢弃这种策略的注解。
-
CLASSClass级别,这是默认策略,编译器会将注解记录到class文件中。
-
RUNTIME运行时级别,注解不仅存在class文件中,而且在运行时可以通过反射获取。
-
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {}
-
@Target@Target注解用来指定被修饰的Annotation可以标记哪些程序元素,与@Retention类似,它的成员变量为一个名为value的ElementType类型的数组,ElementType也是枚举值,常用值如下:-
ANNOTATION_TYPE指定该Annotation只能修饰Annotation:
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface Retention {} -
CONSTRUCTOR指定该Annotation只能修饰构造器
-
FIELD指定该Annotation只能修饰成员变量
-
METHOD指定该Annotation只能修饰方法
-
PARAMETER指定该Annotation只能修饰参数
-
TYPE指定该Annotation可以修饰类、接口(包括Annotation类型)或枚举定义
-
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface MyAnnotation {}
@Documented
使用javadoc工具生成文div后,用@Documented注解标记的Annotation也会显示在文档中。
javadoc -d G:/Temp/api com.strikeback.annotation
@Documented
public @interface MyAnnotation {}
@Inherited
使用@Inherited标记的Annotation具有继承性,即如果某个类使用了用此注解标记的Annotation(A),那么其子类也会有(A)注解。
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {}
@MyAnnotation
public class ParentClass {}
public class ChildClass extends ParentClass{}
Class.forName(ChildClass.class.getCanonicalName()).isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class);//true
三、自定义注解
1、定义
使用@interface关键字可以定义一个新的注解:
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
默认情况下,Annotation可以用于修饰程序中的类、接口、方法、变量等元素。
Annoatation中还可以以无参方法的形式添加成员变量,方法的名称和返回值表示成员变量的变称和类型;在定义变量的同时可以使用default关键字设置其初始值:
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String name();
int count() default 10;
}
如果在Annotation中定了成员变量,而且未设置初始值,那么在使用时要为该成员变量指定值:
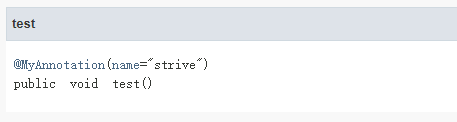
@MyAnnotation(name="strive")
public void test(){
}
如果Annotation中未指定初始值的成员变量只有一个且名称为value,而且在使用时只需指定value的值,此时在使用时可以直接设置value的值,而无需使用key=value形式:
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value();
int count() default 10;
}
@MyAnnotation("strive")
public void test(){
}
2、注解解析
除Annotation接口外,Java在java.lang.reflect包下还提供了AnnotatedElement接口,该接口表示程序中可以接受注释的程序元素,其中Class类、Constructor类、Field类、Method类、Package类都是此接口的实现类。因此,使用反射获取某个类的AnnotatedElement对象(Class、Method等)后,在程中可以调用该对象的以下方法获取Annotation信息:
<T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass)
获取该对象上指定类型的注解。
Annotation[] getAnnotations()
获取该对象上的所有注解。
boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass)
判断该对象是否有指定的注解
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(MyClass.class.getCanonicalName());
//null
System.out.println(clazz.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class));
Method testMethod = clazz.getMethod("test", new Class[]{});
//true
System.out.println(testMethod.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class));
Annotation[] annotations = testMethod.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation annotation : annotations){
//@com.strikeback.annotation.MyAnnotation(name=strive, count=10)
System.out.println(annotation);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}