责任链模式
一、定义
通过让多个对象都有机会去处理请求来避免发送者和接收者之间的耦合。将多个接收者链接起来,并沿着这条链将请求传递下去,直到请求被处理。
二、类图表示
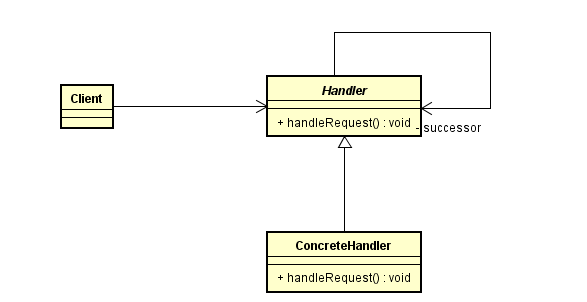
三、实现
package pattern.behavioral.chainofresponsibility;
public abstract class Handler {
protected Handler successor;
public void setSuccessor(Handler successor) {
this.successor = successor;
}
public abstract void handleRequest(Request request);
}
package pattern.behavioral.chainofresponsibility;
public class ConcreteHandlerA extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(Request request) {
if("A".equals(request.getType())){
System.out.println("HandlerA: handling the request " + request);
}else{
System.out.println("HandlerA: passing the request...");
this.successor.handleRequest(request);
}
}
}
package pattern.behavioral.chainofresponsibility;
public class ConcreteHandlerB extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(Request request) {
if("B".equals(request.getType())){
System.out.println("HandlerB: handling the request " + request);
}else{
System.out.println("HandlerB: passing the request...");
this.successor.handleRequest(request);
}
}
}
package pattern.behavioral.chainofresponsibility;
public class ConcreteHandlerC extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(Request request) {
if("C".equals(request.getType())){
System.out.println("HandlerC: handling the request " + request);
}else{
System.out.println("HandlerC: nobody can handle it!");
}
}
}
package pattern.behavioral.chainofresponsibility;
public class Request {
private String type;
private String desc;
public Request(String type, String desc) {
this.type = type;
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%s(%s)", type, desc);
}
}
四、使用
package pattern.behavioral.chainofresponsibility;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Handler handlerA = new ConcreteHandlerA();
Handler handlerB = new ConcreteHandlerB();
Handler handlerC = new ConcreteHandlerC();
handlerA.setSuccessor(handlerB);
handlerB.setSuccessor(handlerC);
handlerA.handleRequest(new Request("A", "give me an apple"));
System.out.println();
handlerA.handleRequest(new Request("B", "turn on the light"));
System.out.println();
handlerA.handleRequest(new Request("C", "close the window"));
System.out.println();
handlerA.handleRequest(new Request("D", "give me a big hug"));
}
}
- 程序输出:
HandlerA: handling the request A(give me an apple)
HandlerA: passing the request...
HandlerB: handling the request B(turn on the light)
HandlerA: passing the request...
HandlerB: passing the request...
HandlerC: handling the request C(close the window)
HandlerA: passing the request...
HandlerB: passing the request...
HandlerC: nobody can handle it!
五、适用场合
-
请求可以被多个接收者处理,但具体是由哪个接收者处理并不确定,需要在运行是确定
-
请求的接收者可能会动态的增加或减少,需要动态指定时